How to improve your account security
TLDR
You already have one or multiple AWS accounts and you want to improve your security approach, the Well-Architected Framework (security pillar) contains a lot of information, I did a full summary here, and you may want to learn about a plan to improve your account.
I will share with you two resources to do it:
- AWS Security Maturity Model will allow you to know the recommended actions to strengthen your security posture at every stage of your journey to the cloud
- Contains 4 phases. The first one,
quick wins, allows you fast security improvements
- Contains 4 phases. The first one,
- Article in the AWS security blog: The top 10 most important cloud security tips that Stephen Schmidt, Chief Information Security Officer for AWS, laid out at AWS re:Invent 2019
AWS Security Maturity Model
It is a valuable resource for reviewing the current status and improving the security of your solutions.
The classification of the different recommendations into categories depends on the cost and difficulty of implementing the security control, and the positive impact that it will achieve.
This model is updated monthly by AWS. In fact, a month after writing this article I had to update it because the model had changed and all areas of the organization had changed, although the content is the same.
The official documentation is located here
Introduction
Security Frameworks
Multiple frameworks help you design the construction of a plan to provide security to your loads in the cloud.
- Well Architected Framework
- NIST CyberSecurity Framework
- Center for Internet Security (CIS) AWS Foundations
- Cloud Adoption Framework
How to prioritize
“With so many services, security controls, and recommendations… How do I prioritize? Where do I start?”
All Quick Win recommendations can be implemented in less than a week.
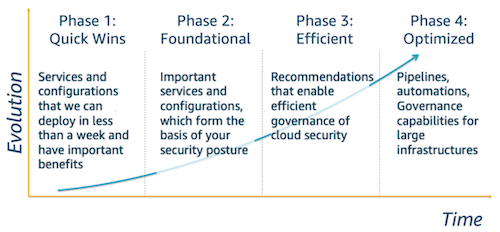
Evolutive path
Phase 1. Quick Wins
Quick Wins are the first thing to focus on, controls that you could implement in an organization within a maximum of one or two weeks, and will significantly improve your security standpoint.
| Level | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Security governance | - Assign Security Contacts - Select the region(s) |
| Security assurance | - Automate alignment with best practices using AWS Security Hub |
| Identity and Access management | - Multi-Factor Authentication - Avoid using Root and audit it - Access and role analysis with IAM Access Analyzer |
| Thread detection | - Thread Detection with Amazon GuardDuty and review your findings - Audit API calls with AWS CloudTrail - Remediate security findings found by AWS Trusted Advisor - Billing alarms for anomaly detection |
| Vulnerability management | |
| Infrastructure protection | - Limit Security Groups |
| Data prevention | - Amazon S3 Block Public Access - Analyze data security posture with Amazon Macie |
| Application security | - AWS WAF with managed rules |
| Incident response | - Act on Amazon GuardDuty findings |
Link to the updated content and more information on each recommendation
Phase 2. Foundational
The controls and recommendations may take some more effort to implement but are very important.
| Level | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Security governance | - Identify security and regulatory requirements - Identify the most sensitive data (crown jewels) - Cloud Security Training Plan |
| Security assurance | - Configuration monitoring with AWS Config |
| Identity and Access management | - Centralized user repository – Organization Policies (SCPs) |
| Threat detection | - Investigate most Amazon GuardDuty findings |
| Vulnerability management | - Manage vulnerabilities in your infrastructure and perform pentesting - Manage vulnerabilities in your application |
| Infrastructure protection | - Manage your instances with Fleet Manager - Network segmentation (Public/Private Networks - VPCs) - Multi-account management with AWS Control Tower |
| Data protection | - Data Encryption (AWS KMS) - Backups - Discover sensitive data with Amazon Macie |
| Application security | - Involve security teams in development - No secrets in your code AWS Secrets Manager |
| Incident response | - Define Incident response playbooks - Redundancy using multiple Availability Zones |
Link to the updated content and more information on each recommendation
Phase 3. Efficient
There are some controls and recommendations that allow us to manage security efficiently.
| Level | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Security governance | - Perform thread modelling |
| Security assurance | - Create your reports for compliance (such as PCI-DSS) |
| Identity and Access | - Privilege review (Least Privilege) - Tagging strategy - Customer IAM: security of your customers |
| Threat detection | - Integration with SIEM/SOAR - Network Flows analysis (VPC Flow Logs) |
| Vulnerability management | - Security champion in development |
| Infrastructure protection | - Image Generation Pipeline - Anti-Malware/EDR - Outbound Traffic Control - Use abstract services (Serverless) |
| Data protection | - Encryption in transit |
| Application security | - WAF with custom rules - Shield Advanced Advanced DDoS Mitigation |
| Incident response | - Automate critical and most frequently run Playbooks - Automate deviation correction in configurations -Using infrastructure as Code (CloudFormation, CDK) |
Link to the updated content and more information on each recommendation
Phase 4. Optimized
And finally, there are those controls and recommendations that allow you to optimize in a continuous improvement cycle, the security posture every day. It will be characterized by security controls that are often seen in more mature organizations, in terms of security or large organizations with very demanding requirements.
| Level | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Security governance | - Forming a Chaos Engineering team (Resilience) - Sharing Security work and responsibility |
| Security assurance | |
| Identity and Access management | - Context-based access control - IAM Policy Generation Pipeline |
| Threat detection | - Amazon Fraud Detector - Integration with additional Intelligence Feeds |
| Vulnerability management | |
| Infrastructure protection | - Process standardization with Service Catalog |
| Data protection | |
| Application security | - DevSecOps - Forming a Red Team (Attacker’s Point of View) |
| Incident response | - Automate most playbooks - Amazon Detective: Root cause analysis - Forming a Blue Team (Incident Response) - Multi-region disaster recovery automation |
Link to the updated content and more information on each recommendation
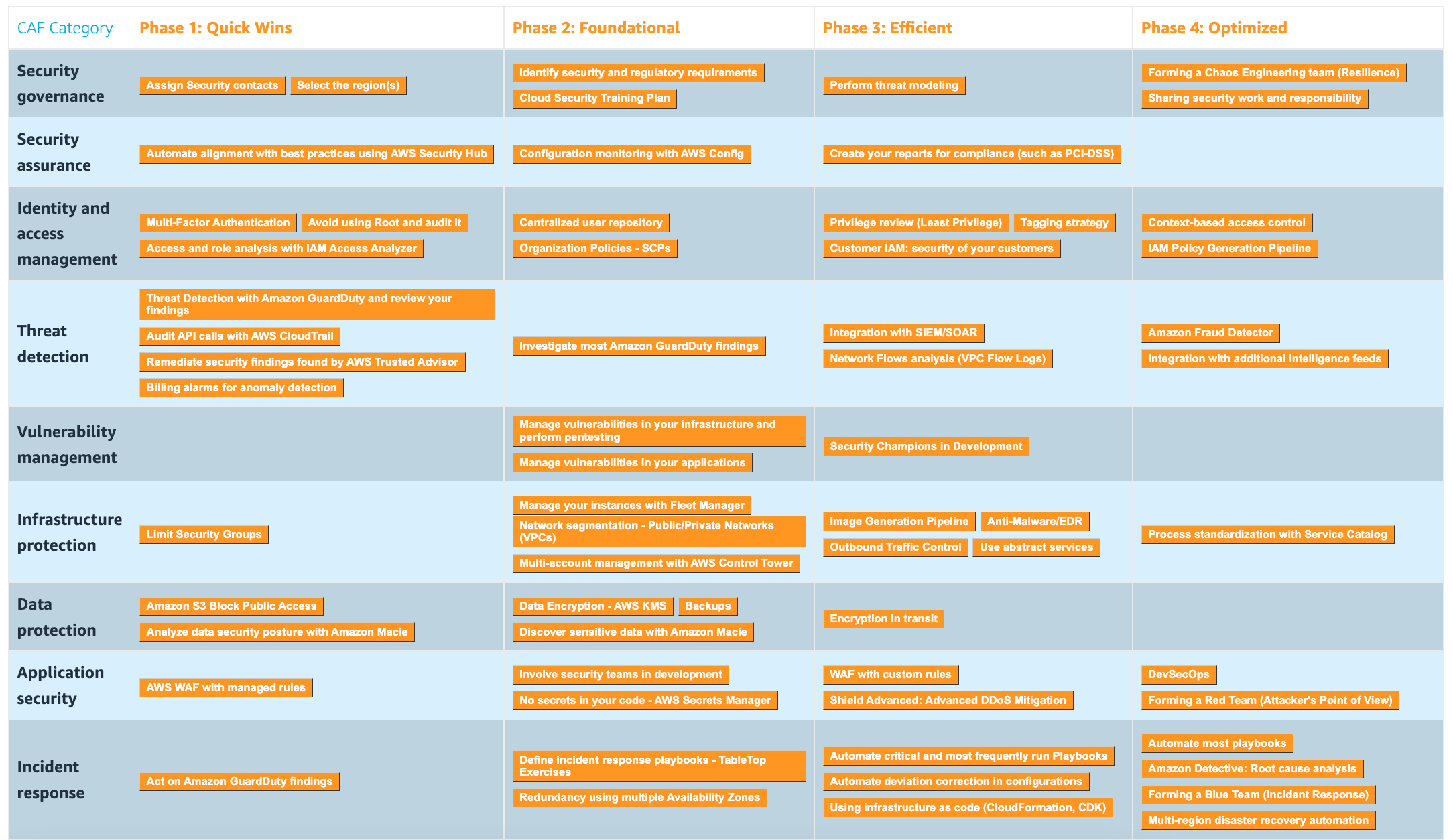
Complete Maturity Level
This is the complete maturity model with all the phases through all the epics.
I recommend you access to the original page to view the linkable table in the original site.
Top 10 recommendations
These are the top 10 most important cloud security tips that Stephen Schmidt, Chief Information Security Officer for AWS, laid out at AWS re:Invent 2019.
The original article was written in the AWS blog here
- Configure account contacts
- Use multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- is the best way to protect accounts from inappropriate access
- No hard-coding secrets
- use AWS Secrets Manager
- if you are using Java or Python you can use CodeGuru Reviewer to detect secrets in the code
- Limit security groups
- use AWS Config and AWS Firewall Manager to programmatically ensure that the virtual private cloud (VPC) security group configuration is what you intended
- Intentional data policies
- design your approach to data classification
- Centralize CloudTrail logs
- AWS recommends that you write logs in an AWS account designated for logging (Log Archive).
- The permissions on the bucket should prevent the deletion of the logs, and they should also be encrypted at rest. Review how to use AWS to visualize AWS CloudTrail logs
- Validate IAM roles
- Use AWS IAM Access Analyzer
- Take action on findings
- Turn on AWS Security Hub, Amazon GuardDuty, and AWS Identity and Access Management Access Analyzer
- You also need to take action when you see findings
- Rotate keys
- Be involved in the dev cycle
- “raise the security culture of your organization.”