Getting Started with AWS AppSync: A Practical Approach to GraphQL
This article is part of a series about
appsync, in which I will explain what is AWS AppSync and how you can use it in your architectures.1/2: Getting started: A Practical Approach to GraphQL
1. Introduction to GraphQL and AWS AppSync
In the ever-evolving landscape of web and mobile application development, efficiency and real-time capabilities are not just nice-to-have features, they’re essential. This is where GraphQL and AWS AppSync come into play, offering developers the tools to build dynamic, scalable applications with ease.
GraphQL, developed internally by Facebook in 2012 and publicly released in 2015, is a query language for APIs and a runtime for executing queries using a type system defined for your data. Unlike traditional REST APIs that require loading from multiple URLs, GraphQL APIs fetch all the data your app needs in a single request, ensuring efficiency even on slow mobile network connections.
AWS AppSync is the GraphQL of AWS. It is a managed service that simplifies application development by creating serverless GraphQL and Pub/Sub APIs. It provides a single endpoint to securely query, update, or publish data, enabling developers to build interactive, feature-rich applications.
1.1. Key Features of GraphQL
Efficient data retrieval: Clients can request exactly what they need, not more, not less. This eliminates over-fetching and under-fetching problems commonly encountered in REST APIs.Single endpoint: GraphQL APIs use a single endpoint to handle queries, mutations (changing data), and subscriptions (real-time updates), simplifying the data fetching process.Strongly typed: The service defines a set of types that completely describe the set of possible data you can query, enabling introspection for documentation and validation purposes.Real-Time data with subscriptions: GraphQL supports real-time updates through subscriptions, enabling live updates to the client as data changes.Declarative data fetching: Clients describe their data requirements as what they need, rather than how to fetch it. This allows for a more declarative approach to data fetching and separation of concerns between client and server.
1.2. GraphQL operations
We have 3 different operations in GraphQL:
- Query: Used to retrieve the data, like GET request.
- Mutation: Used to modify data, like CREATE, UPDATE or DELETE.
- Subscription: Used to subscribe to the changes of data, and receive real-time notifications.
1.3. Why Choose AWS AppSync?
AWS AppSync goes beyond offering standard GraphQL features by integrating deeply with the AWS ecosystem, providing:
Real-time data: Supports subscriptions for real-time data updates to application clients.Offline support: Offers built-in capabilities for offline data access and synchronization, enhancing app reliability and user experience.Direct integration with one or more sources: Seamlessly connects with NoSQL data stores, relational databases, HTTP APIs, and more, enabling complex data aggregation and access patterns.Fine-grained access control: Allows for precise access controls, integrating with AWS IAM and Amazon Cognito for comprehensive authentication and authorization mechanisms.
1.4. Use cases
- Creating a simple Pub/Sub API
- Instantly create APIs for your databases
- Combine multiple data sources into a single GraphQL API
- Real-Time Collaborative Applications
- Data-Driven Mobile and Web Applications
- IoT and Streaming Data Applications
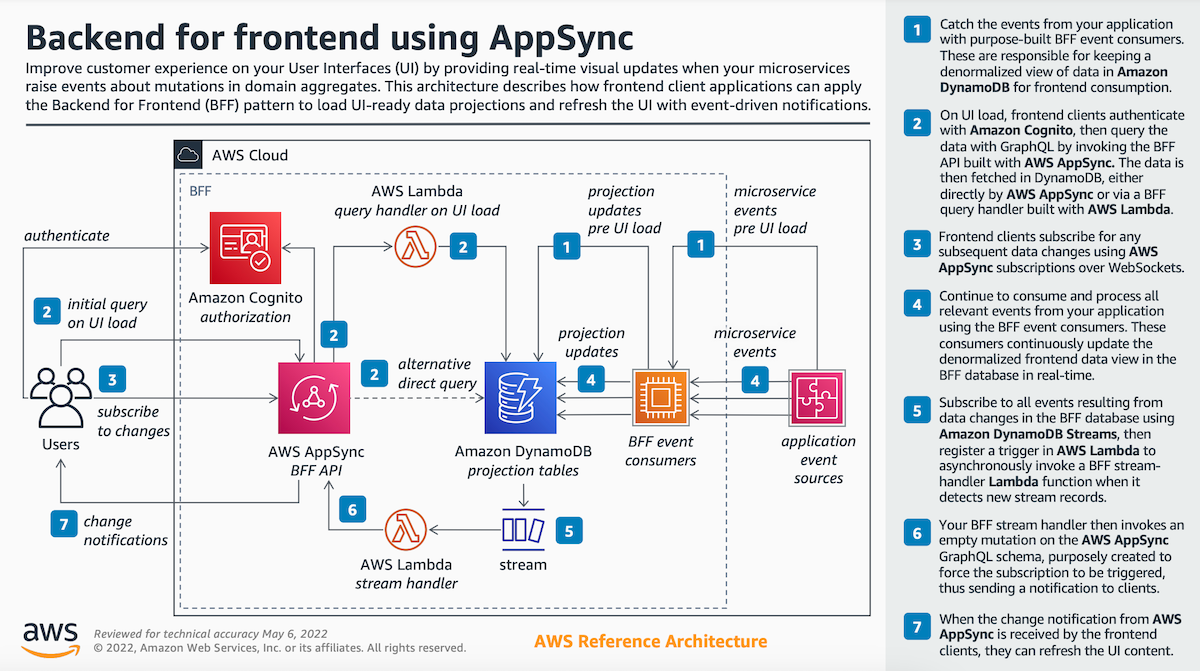
1.5. Example: BFF AWS reference architecture
Original link here
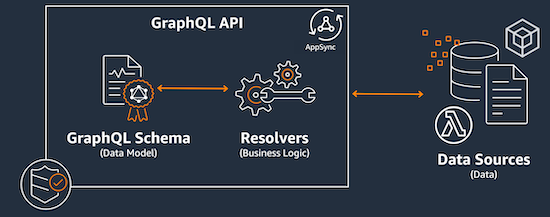
1.6. Components of a GraphQL API
There are 3 main components in a GraphQL API:
Schemas: It is a gateway that handles all requests made to the server. When a request is made, the schema acts as the single endpoint that interfaces with the client. The schema will access, process, and relay data from the data source back to the client. More details here.Data sources: DynamoDB, Lambda, OpenSearch, HTTP endpoints, EventBridge, Relational databases or None data source. More information here.Resolvers: A unit of code that handles how that field’s data will be resolved when a request is made to the service. More information here.
2. Demo: Setting Up Your First GraphQL API with AWS AppSync
2.1. Creating the simplest GraphQL API
We will try the simplest approach, connecting one DynamoDB table, by following the next steps:
I will use the AWS Console to show you the step-by-step but if you prefer to create the AWS AppSync service using Terraform you can check the code here.
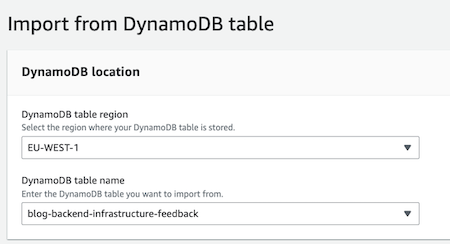
Create a New API: Choose “Create API” and select the “Start with a DynamoDB table” option for this tutorial.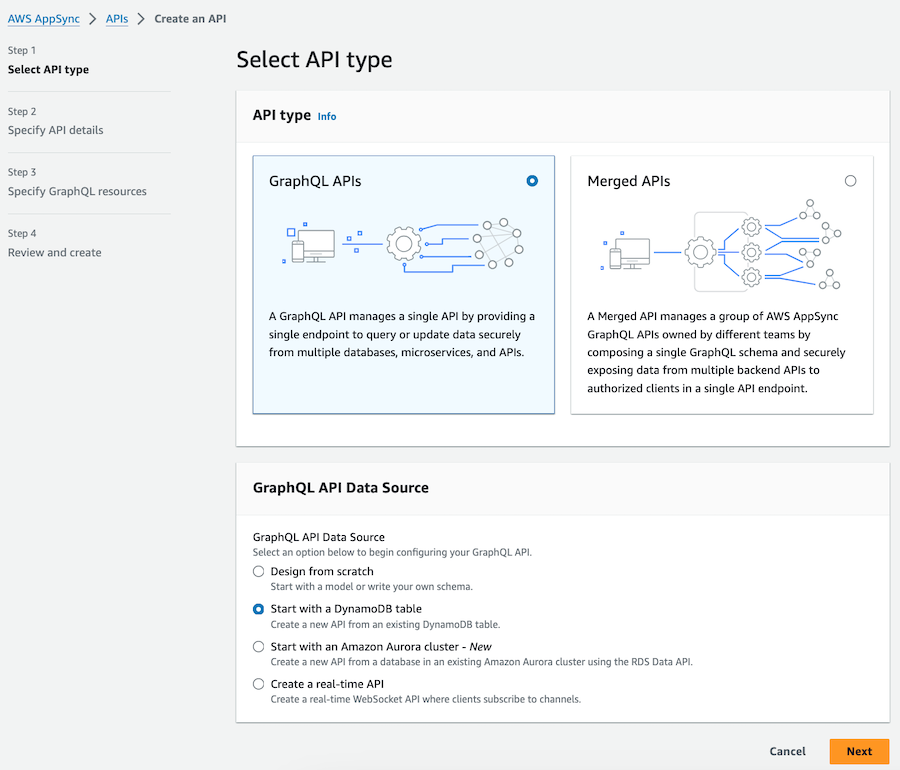
Specify API details: Update all the information here, including “Import from DynamoDB table”. I will use my DynamoDB table in the feedback form of my blog.
Specify GraphQL resources: We have to include all the optional fields in our DynamoDB table.
Create API: Finally, we create the new GraphQL API.
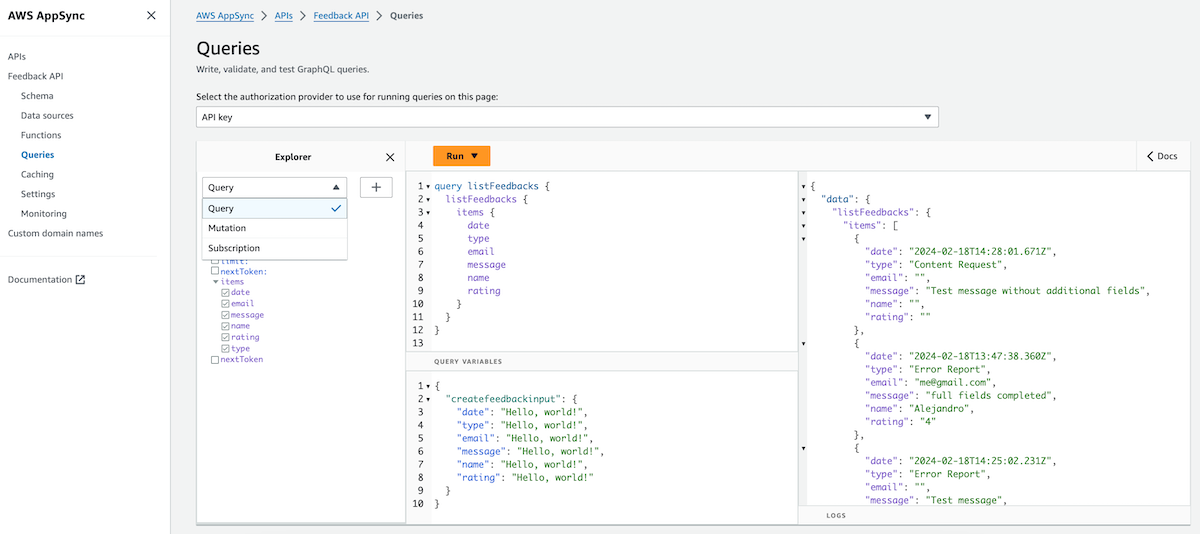
By default, the GraphQL API has been created with all the operations enabled: queries, mutations and subscriptions. We can customize it by changing the Schema.
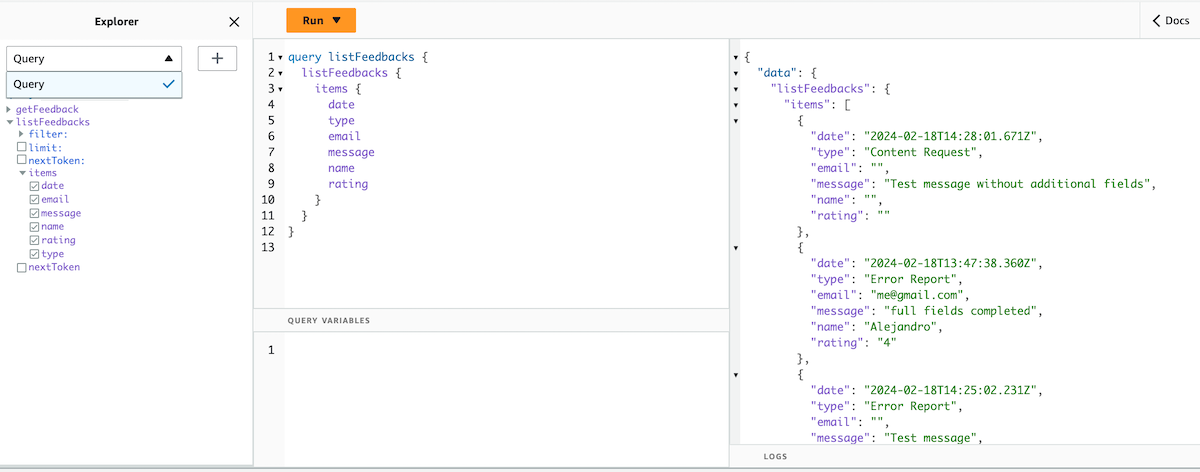
In the Queries section, we can test our API. We can execute Queries, Mutation or Subscription (all the operations were automatically created). In the following example, we will query all the data:
The latest step is to connect our client with the API. Here you will find more information about it.
2.2. Updating the API to only query data
Now, we will update our Schema to only allow query data.
We can use the following schema:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
type Query {
getFeedback(type: String!, date: String!): feedback
listFeedbacks(filter: TableFeedbackFilterInput, limit: Int, nextToken: String): feedbackConnection
}
type feedback {
date: String!
type: String!
email: String
message: String!
name: String
rating: String
}
input TableFeedbackFilterInput {
date: TableStringFilterInput
type: TableStringFilterInput
email: TableStringFilterInput
message: TableStringFilterInput
name: TableStringFilterInput
rating: TableStringFilterInput
}
input TableStringFilterInput {
ne: String
eq: String
le: String
lt: String
ge: String
gt: String
contains: String
notContains: String
between: [String]
beginsWith: String
attributeExists: Boolean
}
type feedbackConnection {
items: [feedback]
nextToken: String
}
3. Conclusion
AWS AppSync helps developers to create efficient, scalable, and interactive applications with ease. To simplify it, you can create a single endpoint that allows you to:
- integrate directly with the source retrieving only the desired data
- receive real-time updates